AWG & SWG ⇄ mm Converter
Enter any one value, click the appropriate calculate button — the other values will update.
Understanding the Gauges
What is AWG?
AWG is a geometric scale used in North America. As the number rises, diameter falls at a fixed ratio. It runs from 0000 (4/0) down to 40 AWG.
What is SWG?
SWG originated in the UK. It is a standard list of preferred diameters from 7/0 down to 50 SWG, still common in British specifications.
Takeaway: AWG 36 is not the same as SWG 36. Always confirm in mm before ordering.
Factors to Consider When Specifying Wire Diameter
- Application goal: prioritise particle retention, throughput, stiffness, or visual openness.
- Open area and flow: finer wires raise open area for a given aperture; thicker wires lower it.
- Strength and durability: heavier gauges resist impact and vibration better.
- Material choice: match grade to corrosion, temperature, and hygiene needs.
- Manufacturing tolerances: confirm achievable wire sizes and tolerances before ordering.
- Standards/legacy drawings: convert everything to mm and record the basis (AWG or SWG).
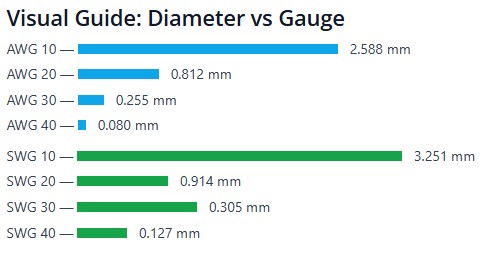
Quick Look: AWG and SWG to mm
| Gauge | AWG (mm) | SWG (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 2.588 | 3.251 |
| 12 | 2.053 | 2.641 |
| 14 | 1.628 | 2.032 |
| 16 | 1.291 | 1.626 |
| 18 | 1.024 | 1.219 |
| 20 | 0.812 | 0.914 |
| 22 | 0.644 | 0.711 |
| 24 | 0.511 | 0.559 |
| 26 | 0.405 | 0.457 |
| 28 | 0.321 | 0.376 |
| 30 | 0.255 | 0.315 |
| 32 | 0.202 | 0.274 |
| 34 | 0.160 | 0.234 |
| 36 | 0.127 | 0.193 |
| 38 | 0.101 | 0.152 |
| 40 | 0.080 | 0.122 |